Organ system
- Several organs unite for a common function and they constitute an organ system.
- Organs of a system function in a coordinated manner to carry out major life processes.
- The body of a vertebrate has nine types of organ system i.e., integumentary system, digestive system, skeletal system, circulatory system, respiratory system, muscular system, nervous system, endocrine system and urinogenital system.
Macrophages
- Macrophages are usually found in a resting state.
- Their phagocytic capabilities are greatly increased when they are stimulated to become activated macrophages.
- The macrophages are present along with lymphocytes in almost all the lymphoid tissues e.g., monocytes as blood macrophages and histocytes as tissue macrophages.
Morphology of earthworm
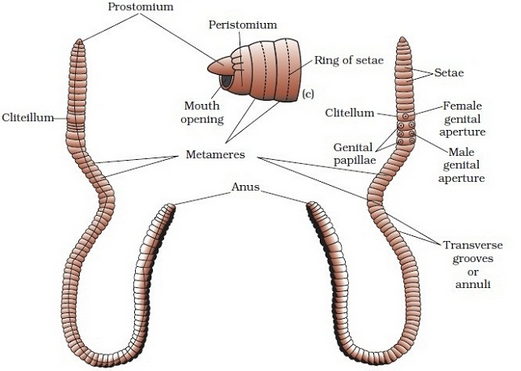
- Earthworms have long cylindrical body, segmented into 100-120 short segments.
- In a mature worm, segments 14-16 are covered by a prominent dark band of glandular tissue called clitellum.
- Except the first, the last and clitellar segments, each segment bears setae which helps in locomotion.
- There are various pores and apertures present in the earthworm. They are for mouth, anus, female genital pore, male genital pore, apertures of accessory glands, spermathecal apertures, nephridiopores and dorsal pores.
Anatomy of earthworm
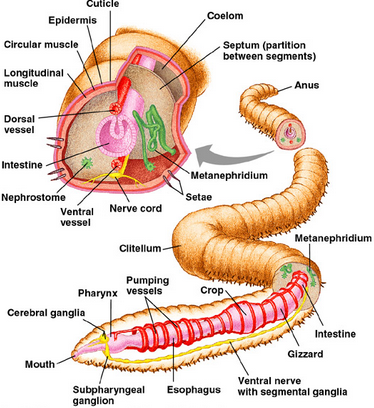
- Body wall of earthworm consists of the cuticle, epidermis, muscular layer and the parietal peritoneum.
- Digestive system of the earthworm consists of alimentary canal (mouth, buccal cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, gizzard, stomach, intestine and anus) and digestive glands (pharyngeal gland, gastric epithelium, intestinal epithelium and intestinal caecae).
- Blood vascular system of earthworm is of closed type.
- Earthworms are both ammonotelic and ureotelic. The main excretory organ is nephridia. Three types of nephridia are found in earthworm namely, the septal nephridia, pharyngeal nephridia, and integumentary nephridia.
Reproduction in earthworm

- Earthworms are bisexual or monoecious or hermaphrodite.
- The male reproductive organ consists of testis sac, testes, seminal vesicles, spermiducal funnels, vasa deferentia, prostate glands and accessory glands.
- The female reproductive organ consists of ovaries, oviducts and spermathecae.
- During copulation, two earthworms get attached through their ventral surface with their anterior end pointing in opposite direction. This leads to exchange of sperms.
- During the process of coccon formation, the membrane receives ova coming from female genital aperture and sperms coming from spermathecal pores. The membrane is laid out on the ground and becomes closed. This structure is called cocoon (ootheca).
Morphology of cockroach
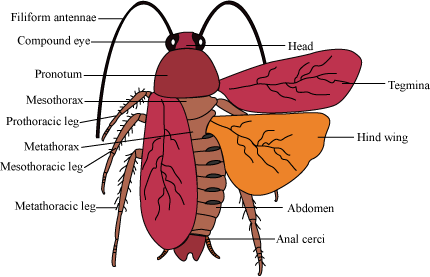
- The cockroach, Periplaneta americana, is a common nocturnal omnivorous household pest, commonly found in damp and warm places.
- The body is elongated, segmented, bilaterally symmetrical, flattened dorsoventrally and reddish-brown in colour.
- It is covered by a hard brown-coloured jointed exoskeleton.
- It is divisible into three parts, head, thorax and abdomen.
- Head consists of 6 segments fused together.
- At its upper side, it bears two large compound eyes.
- A pair of antenna is present in the antero-medial indentation of eyes.
- The mouth is situated at the lower end of the head.
- The mouth parts are of the chewing type, consisting of labrum, mandibles, maxillae, labium and hypopharynx.
- The thorax consists of three segments, an anterior prothorax, a middle mesothorax and a posterior metathorax.
- Each segment bears a pair of walking legs and mesothorax and metathorax also bear each pair of wings.
- The abdomen is broad consisting of ten segments.
Anatomy of cockroach
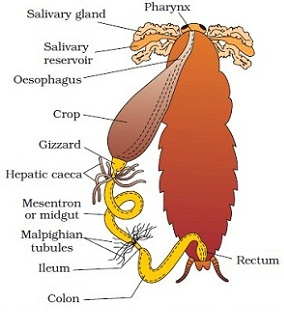
- The body wall of cockroach consists of cuticle, epidermis and basement membrane.
- The body cavity is filled with blood and therefore, called haemocoel.
- The digestive system includes alimentary canal and associated digestive glands.
- The blood vascular system is of open type. The heart is 13 chambered.
- The respiratory system is well developed and consists of spiracles, tracheae and tracheoles.
- The nervous system comprises of central, peripheral and sympathetic nervous system.
- Sense organs include a pair of compound eyes, thigmoreceptors, chemoreceptors, auditory receptors and proprioreceptors.
- The principle excretory organs of cockroach consists of malpighian tubules. Fat bodies and nephrocytes are subsidiary organs of excretion.
Reproduction in cockroach

- The cockroaches are dioecious (unisexual) animals.
- Male reproductive system consists of a pair of testes, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct, utricular gland and phallic gland.
- Female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, oviduct, vagina, genital chamber and colleterial glands.
- Copulation occurs at night during the summer.
- The nymph, hatched from the ootheca, gradually grows into adult through the process of moulting.


Comments
Post a Comment