Uses of algae
- Algae are used as food as they are rich in carbohydrates, vitamins and few other inorganic substances. For example, Spirogyra is the chief source of food.
- Algae release lot of oxygen into water as a by-product of photosynthesis. This is the source of dissolved oxygen for aquatic organisms.
- Agar Agar is used in preparation of ice-cream and jellies. For example, Gelidium.
- Algae are chewed instead of tobacco. For example, Rhodomenia.
- Algae are used extensively in industries to prepare some products like sugar, soap, cement, rubber blotting paper etc.
- Algae are used in agriculture to increase soil fertility. For example, Nostoc, Anabena.
- Some algae are used in the preparation of medicines.
Rhodophyta (red algae)

- They have water soluble red pigment (phycoerythrin), which masks the green color of chlorophyll a.
- The main storage product is floridean starch.
- Sexual reproduction is advanced oogamous type. The male organ produces non motile gametes and the female organ has a long receptive neck. After sexual reproduction special spores are produced.
- For example, Batrachospermum, Polysiphonia.
Phaeophyta (brown algae)

- It contain brown carotenoid, fucoxanthin, which masks the green colour of chlorophyll pigment.
- Most of them are marine.
- The main storage product is laminarin.
- Sexual reproduction ranges from isogamous to oogamous. Motile gametes have two laterally attached flagella. Varied types of alternation of generation.
- For example, Ectocarpus, Sargassum.
Economic importance of Algae
- Algae are used as food as they are rich in carbohydrates, vitamins and few other inorganic substances. For example, Spirogyra is the chief source of food.
- Algae release lot of oxygen into water as a by-product of photosynthesis. This is the source of dissolved oxygen for aquatic organisms.
- Agar Agar is used in preparation of ice-cream and jellies. For example, Gelidium.
- Algae are chewed instead of tobacco. For example, Rhodomenia.
- Algae are used extensively in industries to prepare some products like sugar, soap, cement, rubber blotting paper etc.
- Algae are used in agriculture to increase soil fertility. For example, Nostoc, Anabena.
- Some algae are used in the preparation of medicines.
Division Bryophyta
- Primitive, multicellular, autotrophic, shade loving, amphibious plants.
- Thin, soft, plate like green body (thallus) which is differentiated into stem and leaves or roots (rhizoids) like structures.
- Vascular system absent
- Reproduction: Spore formation
- For example, Funaria, Marchantia, Riccia.
Classification of Pteridophyta
1) Sub-Division - Psilopsida
- These are the oldest known vascular plants. Most of them have become extinct (e.g., Rhynia, Horneophyton). Only two living species, Psilotum and Tmesipteris, are now available.
- Plant body is very simple and does not show much differentiation.
- Dichotomously branched rhizome takes the place of roots.
- Sporangia are directly borne on the stem (i.e., cauline). Either terminal or lateral.
- Plant body shows differentiation into root, stem and leaves.
- Leaves are microphyllous (small) having a single unbranched vein in the midrib region.
- Sporangia are borne in the axil of the fertile leaves.
- Sporophyll form compact strobili (singular strobilus).
- Plant body shows differentiation into nodes and internodes like higher vascular plants.
- Leaves microphyllous, and arise in whorls at each node.
- Sporangia develop on sporangiophores which form compact cones at the apex of fertile branches (e.g., Equisetum).
- Plant body shows much advancement towards higher vascular plants, and is well differentiated into root, stem and leaves.
- Leaves also show great advancement, and are megaphyllous (large) and pinnately compound.
- Sporangia develop on the ventral surface of the sporophylls, and usually aggregated into sori (e.g., Dryopteris, Pteris, Pteridium, Polypodium etc.)
Equisetum
- Habitat of Equisetinae is in moist place. Most of Equisetinae has internodes stems in branch.
- The leaves are small look like membrane and arranged bunches.
- Sporophyl are shield-shaped with amount of sporangium in the bottom.
- Sporangium is arranged conical-shape in tip of the stem or branch. Protalium are green and develop in the outer of their spores.
- For example, Equisetum debile, Sphenophyllum cuneifolium, and Hyenia elegans.
Subkingdom - Phanerogamae
- Flowering plants, plant body is well differentiated into root, stem and leaves.
- Vascular system present.
- Well developed reproductive tissues that make seeds.
- Further classification is based on whether the seeds are naked (gymnosperms) or enclosed in a fruit (angiosperms).
Division - Gymnosperms
- Evergreen, perennial, have unbranched stem and conifer leaves.
- Do not have an outer covering or shell around their seeds i.e., have naked seeds
- Bear separate male and female flowers called as cones.
- Do not produce fruits and flowers.
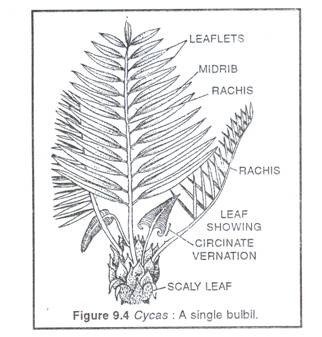
- For example, Pinus, Cycas, Cedrus.
Haplontic life cycle of a plant
- It is characterized by dominant gametophyte and zygotic meiosis.
- The sporophyte generation is represented only by the one-celled zygote, sometimes called zygospore.
- The zygote undergoes meiosis to form haploid spores.
- Each spore germinates (divide mitotically) to form gametophyte.
- Haplontic life cycle found in many algae like Volvox, Spirogyra, Ulothrix, Chlamydomonasetc.
Diplontic life cycle of a plant
- The life cycle characterized by gametic meiosis and diploid sporophyte this is dominant, photosynthetic and independent generation of the plant.
- The gametophyte generation is represented by the haploid gametes or few celled haploid gametophyte.
- Diplontic life cycle is exhibited by some green algae, brown algae and all seed bearing plants i.e., gymnosperms and angiosperms.
- In seeded plants pollens and ovaries contain male and female gametophytes, respectively.
Haplodiplontic life cycle of plant
- This type of life cycle involves the alternation of two vegetative individuals, the haploid gametophyte and diploid sporophyte.
- In this case, sporogenic meiosis occurs in sporophyte to produce spores (meiospores).
- This type of life cycle is exhibited by some green algae, brown algae, bryophytes and pteridophytes.

Comments
Post a Comment